IOT Device Access: Anywhere Example In Computer | Learn Now
Can you truly control an "IoT device from anywhere" with a computer, bending space and time to your digital will? The answer, unequivocally, is yes. This seemingly futuristic capability is not just a pipe dream; it's a tangible reality, reshaping how we interact with the world around us. The power to monitor, manage, and manipulate connected devices from any location with an internet connection has become commonplace, changing the landscape of industries and our everyday lives.
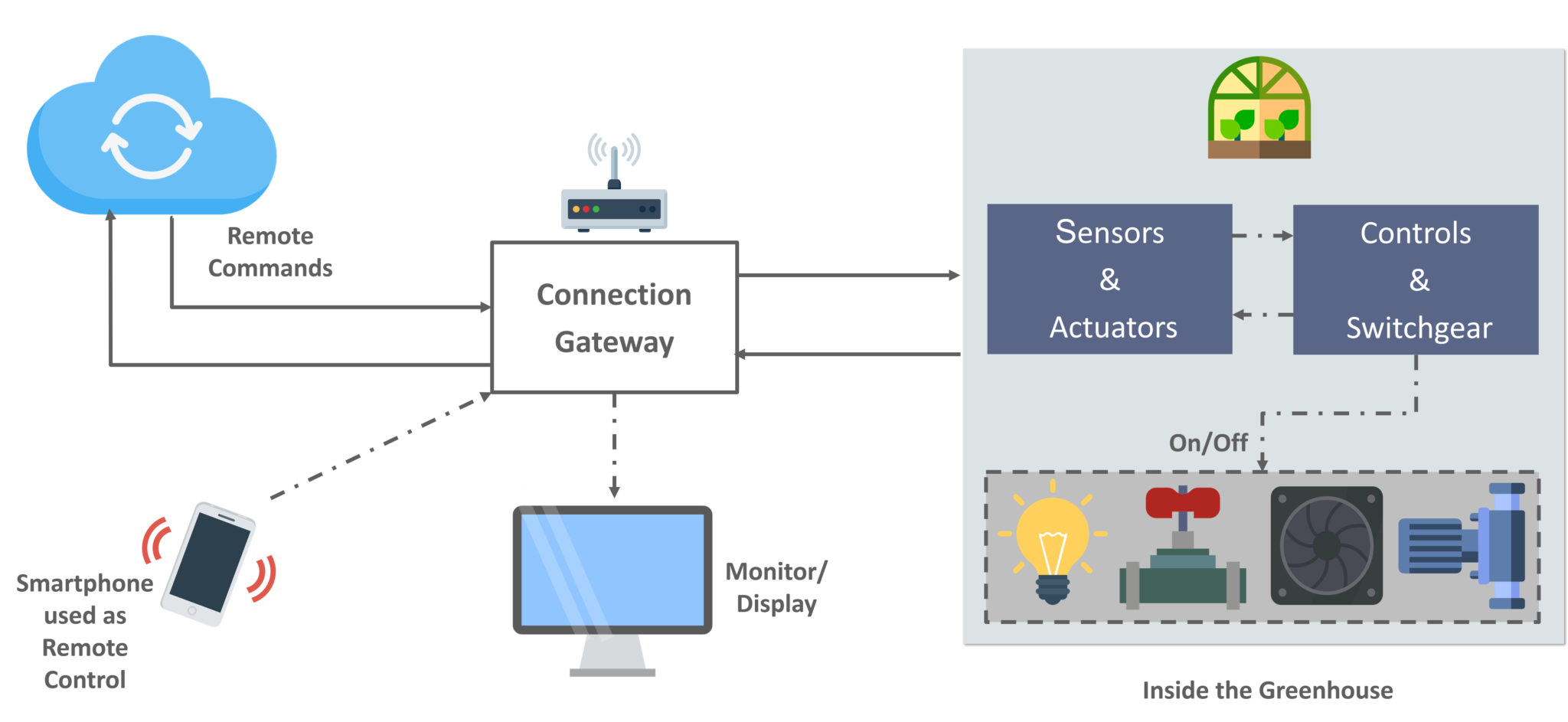
This ubiquitous connectivity, however, is built upon a foundation of complexities. The phrase "IoT device from anywhere" encapsulates a web of technologies and concepts. It starts with the "IoT device" itselfa smart appliance, a sensor, a wearable, or any physical object embedded with sensors, software, and processing capabilities. Next, there's the crucial link: the "computer." This is the central control point, acting as the brain, issuing commands and interpreting data. And, of course, underpinning everything is the "from anywhere" component, meaning the data transfer happens wirelessly. This relies on the internet, cellular networks, or other forms of digital communication to bridge the physical gap between the device and the control center. It's a symphony of hardware, software, and communication protocols, working in perfect harmony, or sometimes, facing disruptive notes from security issues.
Let's delve deeper into the components that make this seemingly magical capability possible. The heart of an IoT device lies in its embedded systema small computer specifically designed for a dedicated task. These systems, often running on microcontrollers, gather information from sensors, process it, and then transmit it. The sensors themselves are the senses of the device, detecting everything from temperature and pressure to movement and light. The communication protocols, like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular connections, are how the device "talks" to the world, sending data to and receiving commands from a central server or directly to your computer. And the computer, well, that is the user interface. This can be a laptop, a smartphone, a tablet, or even a dedicated server, acting as the command center. This control is typically enabled through a web-based dashboard, a mobile application, or a software interface. It allows the user to access real-time data from their device, send commands, and monitor the device's status, whether it's a smart thermostat controlling the temperature or a security camera providing live video feeds.
Consider a practical illustration: a smart home setup. Imagine you're vacationing in Bali. Using your computer (perhaps your laptop or your smartphone), you can access your home's smart hub. Through this hub, you can control your lights, adjusting the brightness or turning them off completely. You can manage your thermostat, ensuring your home stays at a comfortable temperature. If you have a smart security system, you can view live video feeds from your security cameras, offering peace of mind that all is well. These actions, all executed remotely, exemplify the "IoT device from anywhere" concept in action. Another example would be in healthcare. Consider wearable devices that monitor patients' vital signs: blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation. Data from these devices is collected and transmitted to a central server, which is then accessed by doctors and healthcare professionals via computers. This allows for remote patient monitoring, ensuring timely interventions and potentially saving lives. Similarly, in the industrial sector, machines equipped with IoT sensors allow for predictive maintenance. Engineers can monitor the performance of equipment remotely, identify potential issues before they escalate, and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency. Farming practices are evolving because of IoT technology, with farmers using sensors to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and irrigation systems, all controlled from a computer interface. This allows for more efficient water management, reduced resource waste, and improved crop yields. The application of "IoT device from anywhere" is seemingly endless.
However, this innovative concept doesn't come without its challenges. Security is paramount. IoT devices, often deployed with limited security features, become targets for cyberattacks, potentially exposing personal data or compromising the security of entire networks. Furthermore, the interoperability of devices from different manufacturers can be a significant obstacle. Without standardized communication protocols, integrating different devices seamlessly becomes a complex undertaking. Moreover, the sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices, known as "big data", requires robust storage, processing, and analytical capabilities. The devices' continuous operations may lead to excessive energy consumption, and in the long term, the disposal and recycling of large volumes of electronic waste pose environmental concerns. These are important considerations that need to be addressed as the IoT landscape grows and matures.
Let's examine some specific examples to further illustrate the pervasive impact of "IoT device from anywhere":
Smart Homes: As previously mentioned, these systems integrate various devices like thermostats, lights, security systems, and appliances, all controllable via a smartphone or computer, irrespective of the user's physical location. This enhances convenience, improves energy efficiency, and increases home security. Users can monitor and adjust their home environment remotely, creating a tailored living experience.
Smart Cities: Cities are increasingly deploying IoT devices for traffic management, waste management, and environmental monitoring. Sensors collect data on traffic flow, air quality, and waste levels, while city officials analyze these data through their computers, making more informed decisions to improve city efficiency and resident well-being. Streetlights, for example, are being equipped with sensors that automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light conditions, conserving energy and improving safety.
Industrial Automation: This is where the impact is often the most significant. IoT is transforming manufacturing processes with automated equipment and sophisticated production monitoring systems. Real-time data from sensors embedded in machinery is collected and analyzed, allowing for predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency. Factory managers can monitor production output, identify bottlenecks, and make immediate adjustments from any location.
Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring, as noted previously, is improving healthcare outcomes. Wearable devices, medical equipment, and remote monitoring systems are integrated, providing real-time insights into patients' health. Doctors and nurses can remotely monitor vital signs, administer medications, and provide medical interventions, thereby enhancing patient care and potentially saving lives.
Agriculture: Precision agriculture is also benefiting from IoT technology. Sensors monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and irrigation systems, enabling farmers to optimize resource usage and maximize crop yields. Real-time data and remote control capabilities from computers allow farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, making agricultural practices more efficient.
Retail: IoT is transforming the retail experience. Smart shelves track inventory levels, while in-store beacons deliver personalized offers to customers, enhancing their shopping experience. Retailers analyze data generated by these devices to optimize product placement, tailor marketing campaigns, and improve overall store performance. This technology provides opportunities for retailers to better understand their customers and tailor their offerings to meet their needs.
The evolution of "IoT device from anywhere" is a testament to human ingenuity and the constant drive to improve the efficiency and convenience of our lives. It presents exciting possibilities in numerous fields, from healthcare to transportation, and its constantly evolving as new technologies emerge. This journey also brings forth critical questions regarding security, interoperability, and the ethical implications of widespread data collection. Therefore, as we continue to embrace the power of "IoT device from anywhere," a responsible and thoughtful approach, ensuring robust security measures and addressing privacy concerns, is critical to ensure the continued and beneficial development of this revolutionary concept.